LevelOne GTL-2880 Manual - Page 147
Garp
 |
View all LevelOne GTL-2880 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 147 highlights
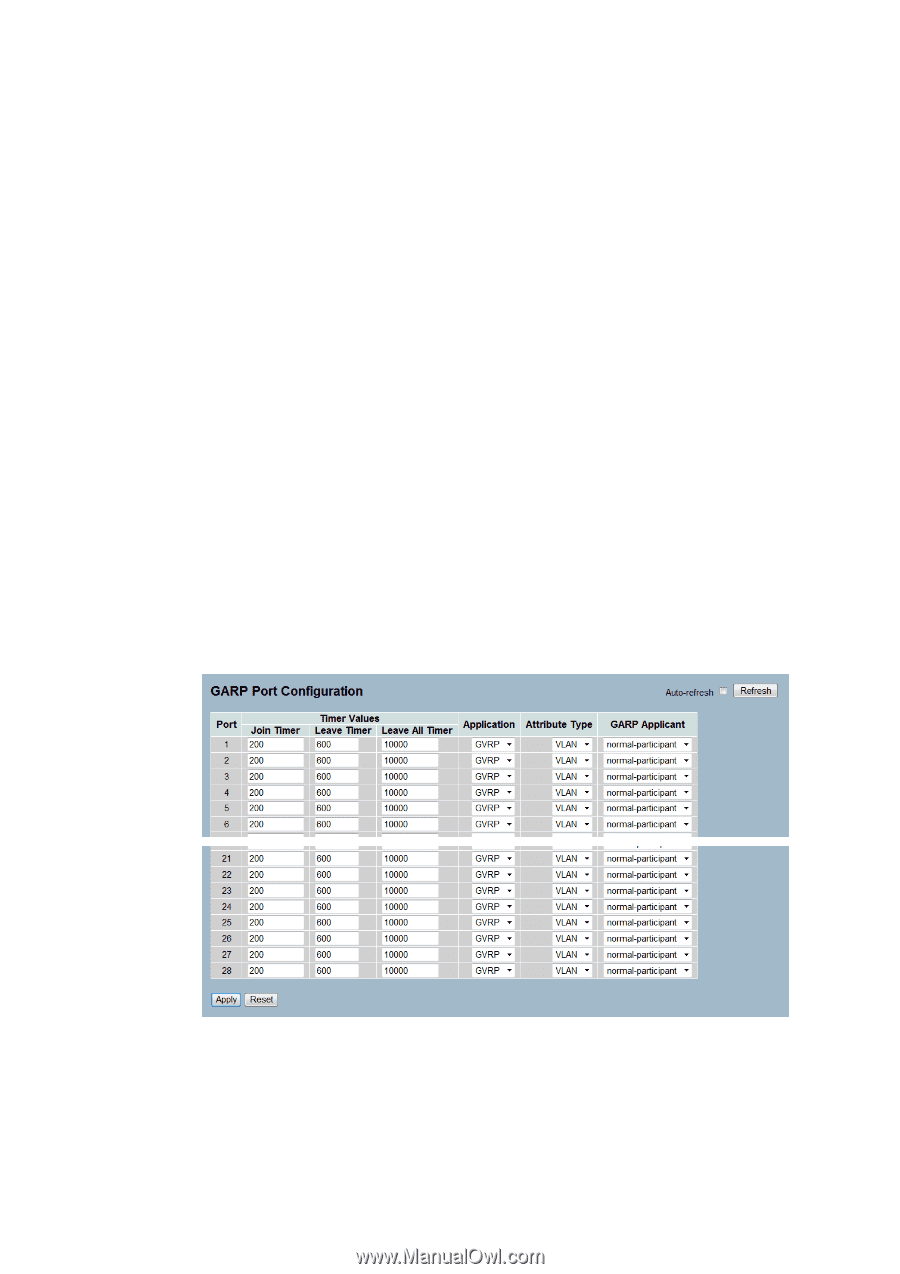
3-12 GARP The Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) provides a generic framework whereby devices in a bridged LAN, e.g. end stations and switches, can register and de-register attribute values, such as VLAN Identifiers, with each other. In doing so, the attributes are propagated to devices in the bridged LAN, and these devices form a ¡°reachability¡± tree that is a subset of an active topology. GARP defines the architecture, rules of operation, state machines and variables for the registration and de-registration of attribute values. A GARP participation in a switch or an end station consists of a GARP application component, and a GARP Information Declaration (GID) component associated with each port or the switch. The propagation of information between GARP participants for the same application in a bridge is carried out by the GARP Information Propagation (GIP) component. Protocol exchanges take place between GARP participants by means of LLC Type 1 services, using the group MAC address and PDU format defined for the GARP application concerned. 3-12.1 Configuration This page allows you to configure the basic GARP Configuration settings for all switch ports. The settings relate to the currently selected unit, as reflected by the page header. Web Interface To configure GARP Port Configuration in the web interface: 1. Click GARP configure. 2. Specify GARP Configuration Parameters.. 3. Click Save. Figure 3-12.1: The GARP Port Configuration Parameter description: Port : The Port coulmn shows the list of ports for which you can configure GARP settings. There are 2 types configuration settings which can be configured on per port bases. Timer Values Applicantion 139