Fantec QB-35RFEU3 Manual - Page 5
Raid O, Raid 1, Raid 3, Raid 5, Raid 10 - 6tb
 |
View all Fantec QB-35RFEU3 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 5 highlights
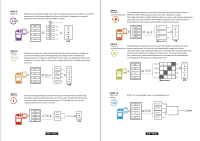
RAID O Spanning Spanning concatenates multiple hard drives as a single large volume; resulting in a seamless expansion of virtual volumes beyond the physical limitations of separately connected hard drives. Thze data are written frim HDD1 to HDD4. 2TB 2TB 2TB 2TB 8TB RAID O Striping Striping is a method of concatenating multiple hard drives into one logical storage unit. It is the automated process of writing data across multiple drives simultaneously. Striping is used to increase the performance of disk reads. The multiple hard drives will write data in "column" effect. If one drive in a striped set fails, all of the data in the stripe set is lost. 2TB 2TB 2TB 2TB 8TB RAID 1 Mirroring Mirroring is the automated process of writing data to multiple drives simultaneously. Mirroring is used to provide redundancy. If one drive fails, the redundant drive(s) will continue to store the data and provide access to it. The failed drive can then be replaced and the drive set can be rebuild. EMPTY EMPTY 2TB MIRRORING 2TB 2TB EN - 07/28 RAID 3 Striped set with dedicated parity This mechanism provides an improved performance and fault tolerance similar to RAID 5 but with a dedicated parity disk rather than rotated parity stripes. The single parity disk is a bottle-neck for writing since every write requires updating the parity data. One minor benefit is the dedicated parity disk allows the parity drive to fail and operation will continue without parity or performance penalty. 2TB 2TB EMPTY 2TB XOR PARITÄT 4TB RAID 5 Striped set Distributed parity requires all drives but one to be present to operate; drive failure with distributed parity requires replacement, but the array is not destroyed by a single drive failure. Upon drive failure, any subsequent reads can be calculated from the distributed parity such that the drive failure is masked from the end user. The array will have data loss in the event of a second drive failure and is vulnerable until the data that was on the failed drive is rebuilt onto a replacement drive. XOR PARITÄT 2TB 2TB 2TB 2TB 6TB RAID 10 Mirroring + Striping RAID 10 is mirrored(Raid 1) sets in a striped(Raid 0) set . 2TB MIRRORING 2TB 2TB MIRRORING 2TB STRIPING 4TB EN - 08/28